If your house is too humid, there are many consequences because your home’s relative humidity should be between 30-50% to avoid dust mite infestation, condensation on your water pipes, wet stains on your walls and ceilings or other unhealthy conditions. With whole home dehumidifiers, your home’s indoor humidity problems can be solved and this can deter mold and mildew growth in your home and the allergic reactions that can happen from excessive moisture conditions.
Whole house dehumidifiers are installed as part of your home’s heating and cooling system, which allows them to pull the air from every room in your home, remove the moisture and then send the dryer air back into your home. You can have whole house dehumidifiers processing the air in your home, even when you aren’t using your heating or air conditioning system. If you have trouble sleeping at night because of clammy skin or you feel like you have to keep lowering the temperature setting because your home feels stuffy, chances are that whole house dehumidifiers could make your home more comfortable.

A whole-house dehumidification system in your home will manage the air’s moisture while in cooling mode, for greater comfort and indoor air quality. This technology can also help reduce the opportunity for mold and mildew problems associated with high humidity levels and minimize the impact of potential airborne pollutants.
How Do They Work?
The same as a smaller model, but on a much larger scale as you can tell. While a standard dehumidifier will consume the surrounding air, remove its moisture and pump it back out, its how whole house dehumidifiers are fitted which differs. Whole house dehumidifiers will be connected to an existing or new cooling/heating/air conditioning system and will use your other vents to its advantage consuming moisture through them.
Benefits of Whole Home Dehumidifier
- Low Maintenance:
Units can be piped into your drainage system so you literally have it installed, turn it on and let it go. Water will be pumped directly out of the house. No more collecting and replacing water trays/buckets. - Improved Health:
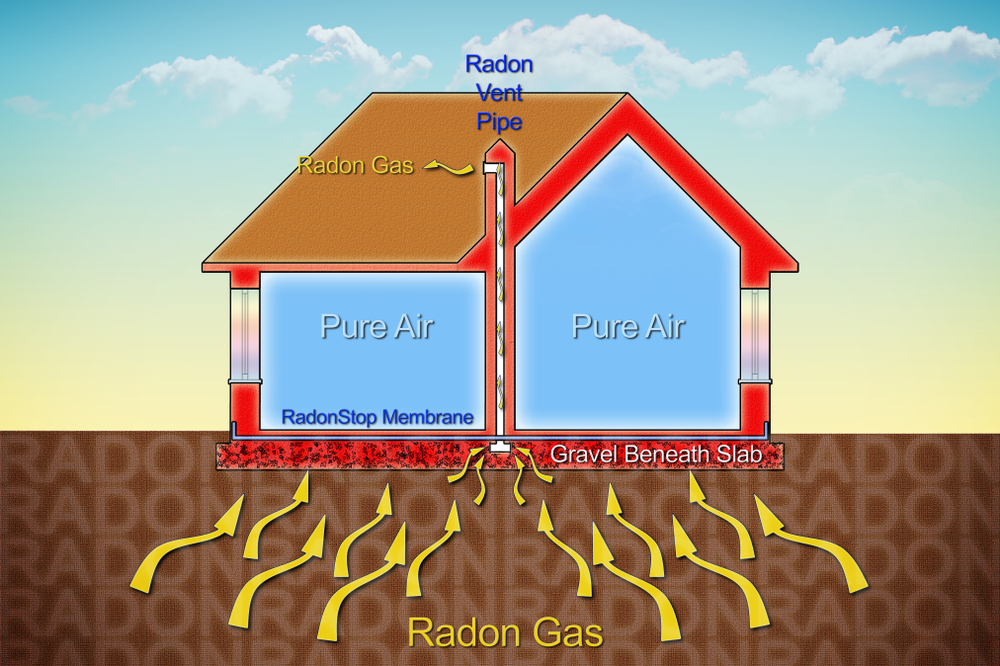
Lowering the humidity in your home eradicates the spreads of mold, mildew and dust mites. No longer will you and your children be forced to breathe in their spores and droppings. Purchase a radon testing kit and when testing, remember that the EPA recommends residences maintain levels below 4 pCi/L, with 1.3 pCi/L being the average. If you do have high radon levels, hire a qualified professional to install a radon mitigation system ($800-$1200). These systems vent the gas directly from the ground to the air outside and can eliminate the majority of your home’s radon. - Clean Air:
Once the humidity levels are controlled the air in your home will no longer seem so heavy. Feel the clean fresh air as it enters your lungs. Breathing will never have felt so refreshing. - Clean Interiors:
With the humidity gone mold and mildew will not attack your clothes, furnishings and house structure. The smell of dampness or ‘wet dog’ as I often hear it called will be gone. Enjoy smelling clean and fresh. You can invite people around once more without being embarrassed. - Damage free decorations and furnishings:
No more throwing out cushions, rugs, curtains and more. You can redecorate with peace of mind knowing that the dampness is gone. You will not have to hide the water stains behind the furniture anymore. - Sleep soundly:
It is a common fact that a house with high humidity is not a place where you can sleep easily. With mold spores, dust mite droppings and dampness filling the air sleep is often restless and fitful. Get rid of those problems with a whole house dehumidifier and sleep will be wonderfully refreshing and sound. - Minimize Radon Exposure Within your Home:
This invisible, radioactive gas is a natural product of uranium decay occurring underground and seeps from the earth into buildings. It’s harmful when humans are exposed to even low levels of it over extended periods of time and is ranked the number 2 cause of lung cancer after tobacco. The worst affected are smokers who have up to 9 times the chance of developing lung cancer when they live in a house with high radon levels. But regardless of whether you smoke or not, protecting yourself from this invisible killer is essential.

Disadvantages of Whole Home Dehumidifiers
- As they are bigger and more advanced than standard units, the cost is greater to run them although it would be cheaper than having multiple portable units spread throughout the home.
- Unless you have the manpower, skills, and knowledge to fit one your self, then you will need to hire an installation team.
The Bottom Line
The bottom line is, if you have full faith that are reliably testing the chemicals in the products you and your family use every day, then you have thousands of mattresses to choose from. Some people believe purchasing more smaller and less expensive units that they can spread around their house is a smart idea, but it is actually more cost effective to bite the bullet and go for a whole house one. Why? Because the cost to run all of those smaller room- sized units will cost you a lot more than to run just the one whole house dehumidifier. Not to mention whole house models will be far more reliable and efficient.